Stanford GSB Essay 2: What do you want to do—REALLY—and why Stanford?
Jul, 19, 2011
Categories: Admissions Consulting | Essays | MBA | MBA留学 | Stanford GSB
Stanford GSB Essay 2 for Admission to the Class of 2014
A good answer to Essay 2 will do the following three things:
2. The applicant’s career goals are believable.
If you have a draft of Essay 2 that does these three things, chances are you don’t need to read this long post. Otherwise, you should.
Before doing anything else, watch this video if you have not done so:
I think this well produced video really does convey the mission of the Stanford MBA program. It also allows you to get a glimpse of the new GSB campus, the Knight Management Center. In June 2011, along with my colleagues from the Association of International Graduate Admissions Consultants, I had a chance to visit the Knight Management Center. Our guide was Derrick Bolton, Assistant Dean and Director of MBA Admissions. Dean Bolton gave us a great tour of the new campus as well as answering our questions. If you can’t visit campus, I do suggest watching this short video as well:
It gives a nice sense of what the GSB campus is now like. I am glad that I had the opportunity to visit the old campus last year, so that I could see how significant this change is in terms of creating a vast and incredibly flexible contemporary space that truly reflects the innovative spirit of the business school. HBS and Chicago Booth have great campuses, but as a Californian, I have to say Stanford’s campus makes incredible use of my home state’s environment.
“What do you want to do—REALLY—and why Stanford?”
Stanford has again changed Essay 2. My analysis has been altered to reflect that change in wording. In essence, the new question is not so different from last year’s
“What are your career aspirations? What do you need to learn at Stanford to achieve them?” because you are still required to discuss what you want to do after Stanford and why you want to go to Stanford.
I think the addition of “REALLY” reflects the fact that Stanford was tired of receiving answers to this question that were simply based on what applicants thought Stanford wanted to hear. I can say that my clients who received invites as well as the those who are admitted are able to put forward goals that do all of the following:
2. Consistent with the applicant’s biography. That is to say, applicants have facts in their past experience that must make their goals believable. I work with reapplicants to Stanford and for those who are dinged without an interview, I frequently find their goals essays lack this consistency. For instance someone who says they want to go into social entrepreneurship, but has no history of getting involved with non-profit organizations, lacks significant recent volunteer experience, and/or has no significant entrepreneurial experience, simply lacks credibility.
Before reading the rest of the post, you might want to take a look at an interview I conducted with a member of the Class of 2010 as a number of his comments relate directly to Essay 2. Those who read Japanese should also take a look at the blog sutebuu survival@Stanford GSB by a member of the Class of 2011, which provides insights into the curriculum and other aspects of life at Stanford. You can find my interview with “Sutebuu” here. Japanese applicants should also see http://stanfordmba-lawyer.blogspot.com/. If you are considering an entrepreneurial career path, please see one of my earlier posts.
THIS IS A FUTURE DIRECTED QUESTION
Unlike some other “Why MBA” questions, Stanford is not asking about the past. You will write about that in the other essays. Instead focus not just on your goals, but on your mission. How will you make a difference and how can Stanford GSB help you do that?
You need to be ambitious. Simply stating what your goals are and why Stanford is the best place for you to accomplish them is not exactly what you need here. Instead, you need to articulate a vision related to your goals and a vision that is connected to Stanford’s mission to train global leaders. For more about writing goals that are both ambitious and visionary, see here.
ARE YOUR GOALS EXCITING?
Making career goals exciting requires thinking about whether your goals are compelling. Admissions committees ask applicants to write about their goals after graduate school, but can applicants actually know what will be on the cutting-edge in two or three years? While many applicants will be able to successfully apply with relatively standard goals (“I want to be a consultant because…”), communicating aspirations requires going beyond the typical.
Be informed. Stanford Admissions needs to believe you know what you are talking about. If you are changing careers, no one expects you to be an expert, but you should come across as having a clear plan based on real research into your future. If you are planning on staying in your present industry, you should be well informed not only about the companies you have worked for, but about the industry as a whole. If you are not already doing so, read industry related publications and network.
Those who are changing fields should most certainly read industry related publications in their intended field. I also suggest conducting informational interviews with at least one peer level and one senior level person in that field. Conduct a peer level interview to get a good idea of what it would be like to actually work in that industry. Conduct a senior level interview to get the perspective of someone who can see the big picture and all the little details as well.
Don’t know anyone in your intended field? Network! One great way to start is through LinkedIn. Another is by making use of your undergraduate alumni network and/or career center.
LEARN WHAT IS HOT. No matter whether you are changing fields or not, learn what is hot now and try to figure out what will be hot by the time you graduate. Now, of course, this is just a plan and chances are that what is hot in your industry or field now may very well be cold in the future. The point is to come across to Stanford as someone who is not only well informed, but has CUTTING-EDGE knowledge. Some great general sources for learning what is hot:
From the Business Schools: Feed your brain with cutting-edge ideas from the best business schools in the world. If you have an iPhone or iPad, you can download the Stanford Business Magazine App for free. You can also read the Stanford Business Magazine online or download it. Most Stanford GSB faculty research papers are available for free in PDF format on the Stanford GSB website at https://gsbapps.stanford.edu/researchpapers/. Other great sources of information include Stanford Social Innovation Review, Harvard Working Knowledge, Harvard Business Review, Harvard Business School Publishing, University of Chicago GSB’s Working Papers, The University of Chicago’s Capital Ideas, Knowledge @ Wharton, and MIT Sloan Management Review.
You may also want to do a search on itunes for podcasts: My favorites are Entrepreneurial Thought Leaders (from the Stanford School of Engineering, but totally relevant to the GSB), Chicago GSB Podcast, Net Impact, and Harvard Business IdeaCast. INSEAD, IMD, LBS, and Wharton also have podcasts.
LinkedIn Answers: I would suggest that everyone join LinkedIn and make use of LinkedIn Answers. LinkedIn Answers is a great way to tap into cutting edge expertise. Follow LinkedIn’s rules and you will often be able to obtain excellent information.
Hoovers: For information about specific companies, Hoovers is just a great way to learn about key facts including competitors (a very useful way of knowing who else you might want to work for and to learn about an industry). While primarily focused on the US, Hoovers does have listings for companies worldwide.
Vault: For scope of coverage, this site is a must. Vault includes both career and admissions information. It includes both company specific and industry-wide information.
Other sources: Read magazines, websites, and books that relate to your intended field.
DOES IT ALL MAKE SENSE?When formulating goals, the necessary prerequisite for formulating aspirations, I suggest going through a formal process of goals analysis.
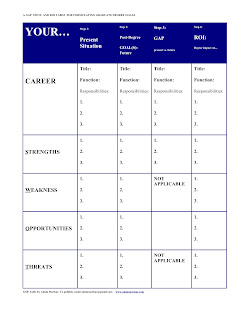
You can use my GAP, SWOT, AND ROI TABLE FOR FORMULATING GRADUATE DEGREE GOALS for this purpose (see below). I think Gap, SWOT, and ROI analysis are great ways for understanding what your goals are, why you want a degree, and how you will use it. (Click here for a GMAC report on MBA ROI. )
(To best view the following table, click on it.)
Step 1. Begin by analyzing your “Present Situation.” What job(s) have you held? What was/is your functional role(s)? What was/are your responsibilities?
Next, analyze your present strengths and weaknesses for succeeding in your present career. REMEMBER:WHEN YOU ARE THINKING ABOUT YOUR STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESS DON’T ONLY THINK ABOUT WORK, THINK ABOUT OTHER ASPECTS OF YOUR LIFE. In particular, some of your greatest strengths may have been demonstrated outside of work, so make sure you are accounting for them.
Strengths: What are you good at? Where do you add value? What are you praised for? What are you proud of?
Weakness: What are you bad at? What are you criticized for? What do you try to avoid due to your own limitations? What do you fear?
Next, analyze the environment you work in right now. What opportunities exist for your growth and success? What threats could limit your career growth?
Step 2. Now, do the same thing in Step 1 for your “Post-Degree” future after you have earned your graduate degree. IF YOU CANNOT COMPLETE STEP 2, YOU HAVE NOT SUFFICIENTLY PLANNED FOR YOUR FUTURE and therefore you need to do more research and need to think more about it.
Step 3. If you could complete step 2, than you should see the “Gap” between your present and your future. What skills, knowledge, and other resources do you need to close the gap between your present and future responsibilities, strengths, and opportunities?
Step 4. After completing Step 3, you now need to determine how an MBA will add value to you. It is possible that an increased salary as a result of job change will be sufficient “ROI” for the degree to justify itself, but you should show how a degree will allow you to reach your career goals. How will the degree enhance your skills and opportunities and help you overcome your weaknesses and external threats? If you can complete Step 4 than you should be ready to explain what your goals are, why you want a degree, and the relationship between your past and future career, as well as your strengths and weaknesses.
The above table will also help you answer such common interview questions as: Where do you want to work after you finish your degree? Why do you want an MBA (or other degree)? What are you strengths? What are your weaknesses? What are your goals? Thinking about these issues now will help you to develop a fully worked-out strategy for how you will best present yourself both in the application and in an interview.
“and why Stanford?”
Your objective in the essay is demonstrate why you would greatly benefit from a Stanford MBA education. Actually without that, your aspirations will not make sense because you must have career goals that require Stanford. Assume that for your goals to be effective, Stanford admissions has to make the determination that you are someone who will make best use of their resources. Stanford is proud of what they are and what they can offer. They can reject anyone and they do reject a higher percentage of applicants than other schools. Keep in mind what Derrick Bolton, the Director of Admissions, says about Stanford Essay 2:
How do you plan to take advantage of the incredible opportunities at Stanford? How do you envision yourself contributing, growing, and learning here at the Business School? And how will the Stanford experience help you become the person you described in the first part of Essay B [Essay 2]?
One thing I think that separates great versions of Essay 2 (the ones that get applicants an interview) and mediocre versions (the ones that usually don’t get applicants an interview) is the extent to which the applicant is able to show that Stanford is not a mere afterthought or an option, but actually a necessity to accomplish one’s aspirations. Fully account for that in your essay. Learn as much as you can about the program and think deeply about who it will impact you. Stanford views itself as a change agent. Show in you essay how it will change you.
The writing process: After going through a process of reflection and analysis, prepare a version of Essay 2 that includes everything you want to say. Next begin the process of revision. Here are a few key things to consider when revising:
1. Think about the most important thing you need admissions to know about what you want to do after your MBA and why Stanford GSB is the best place for you to do that. Begin your essay with that. Chances are good that on your initial draft the most important thing is somewhere in the middle or end of your essay.
2. Prioritize the rest of your content: What do they really need to know? Chances are you have lots of details that can be cut.
3. Make a formal argument: Your essay should be neither a set of disembodied points or a summary, instead it should be a formal statement. Effective forms of this statement vary. The important part is that the reader should be able to understand it clearly and be convinced by it.
Once you have put together Essay 2, consider how the rest of your application supports what you say in it. Without over-marketing yourself or even necessarily writing it directly in the essays, make that your other essays and other aspects of your application show how your potential will contribute to your future aspirations.
-Adam Markus
スタンフォード ビジネススクール カウンセリング コンサルティング 大学院 エッセイMBA留学